
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
High-Quality Thread Rolling Machines for Efficient 3 Die Production
The Advantages of 3% Die Thread Rolling Machines in the Manufacturing Sector
In the world of manufacturing, the demand for precision and efficiency is ever-increasing. One of the critical processes that significantly contribute to these demands is thread rolling, particularly with machines that utilize a die rolling system. Among the various options available, 3% die thread rolling machines have emerged as notable choices for companies seeking to enhance their production capabilities. This article delves into the features, advantages, and applications of 3% die thread rolling machines.
What is a 3% Die Thread Rolling Machine?
A 3% die thread rolling machine is designed to create threads on metal rods and components efficiently. The term 3% die refers to the specific configuration of the dies used in the machine, which allows for precise shaping of the threads. Unlike traditional cutting methods, die rolling forms threads by displacing the material rather than removing it. This process not only improves the durability of the threads but also enhances the overall efficiency of production.
Key Advantages
1. Increased Strength and Durability
One of the primary benefits of using a 3% die thread rolling machine is the enhanced strength of the finished threads. The cold working process involved in thread rolling aligns the grain structure of the metal, leading to improved tensile strength. This characteristic is vital in applications where components must withstand high stress and wear, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
2. Superior Surface Finish
Thread rolling produces a finer surface finish compared to conventional cutting methods. The displacement of material creates smoother threads, reducing the chances of stress concentration points that can lead to failure. This excellent surface quality is particularly advantageous for components requiring tight tolerances and those subjected to corrosive environments.
3. Higher Material Utilization
3 die thread rolling machine products
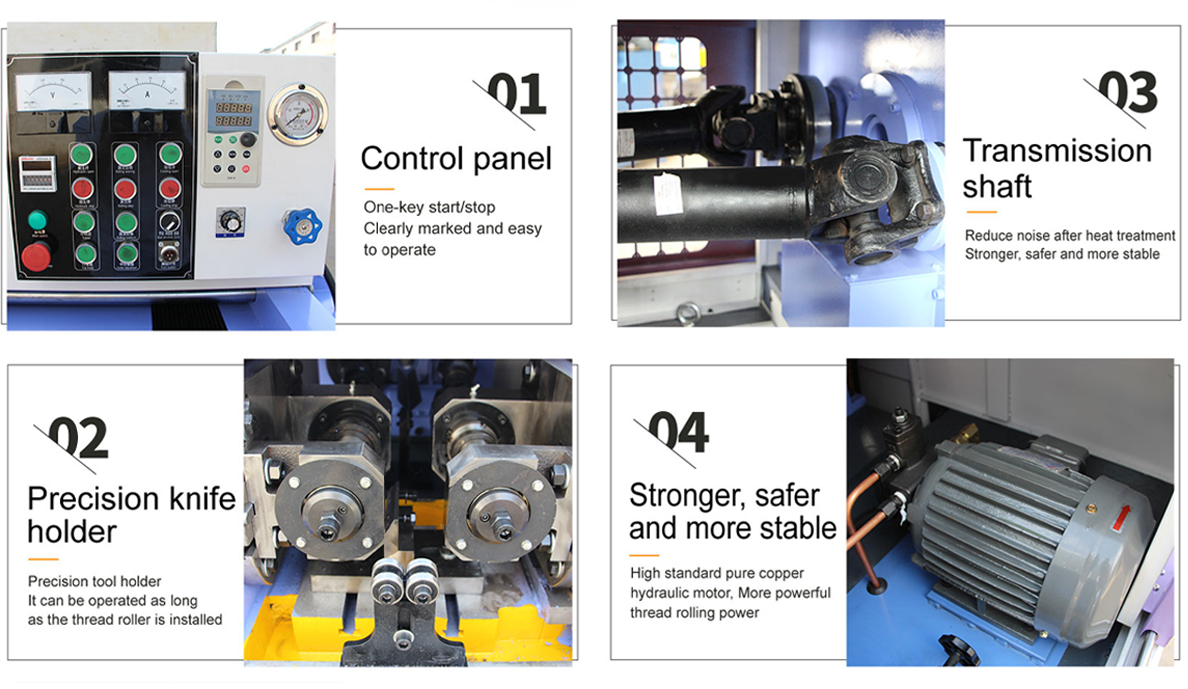
Traditional machining processes often result in significant material wastage due to cutting and shaping. Conversely, thread rolling minimizes material loss, with studies indicating that it utilizes up to 98% of the original material. This efficiency is a crucial consideration for manufacturers focused on sustainability and cost-effectiveness, allowing for lower raw material costs and reduced waste.
4. Increased Production Efficiency
3% die thread rolling machines are capable of producing threads at a much faster rate than machining processes. The rapid production speeds enable manufacturers to meet high-volume demand without sacrificing quality. Additionally, the automation capabilities of modern rolling machines further enhance efficiency, reducing labor costs and minimizing the risk of human error.
5. Versatility
Another advantage of these machines is their versatility. They can work with a wide variety of materials, including aluminum, steel, and even softer metals, making them suitable for numerous applications across various industries. From creating bolts and screws to manufacturing specialized fasteners, 3% die thread rolling machines can meet diverse production needs.
Applications in Various Industries
The applications of 3% die thread rolling machines are extensive. In the automotive industry, they are used to produce components like wheel bolts and engine parts that require high strength and durability. The aerospace sector benefits from the lightweight yet strong components made possible by thread rolling. Similarly, in the construction industry, these machines produce secure and reliable fasteners critical for structural integrity.
Conclusion
The adoption of 3% die thread rolling machines is revolutionizing manufacturing processes across various sectors. With their ability to produce durable, high-quality threads efficiently and with minimal waste, these machines offer significant advantages over traditional methods. As the industry continues to prioritize efficiency and sustainability, the use of 3% die thread rolling machines represents a forward-thinking solution that meets the demands of modern manufacturing. Investing in this technology not only enhances production capabilities but also supports a more sustainable approach to manufacturing, making it a worthwhile consideration for manufacturers worldwide.
