
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Exploring HS Code for Thread Rolling Machine Exporters and Their Market Trends and Opportunities
Understanding the Export Dynamics of Thread Rolling Machines An Insight into HS Codes
In the realm of manufacturing and metalworking, thread rolling machines play a pivotal role in the production of threaded fasteners and components. These machines are essential for creating high-strength threads without the need for cutting, which enhances the durability and performance of the finished products. As global trade continues to expand, understanding the export dynamics of thread rolling machines, particularly through the lens of Harmonized System (HS) codes, becomes crucial for manufacturers and exporters alike.
The Role of HS Codes
HS codes, or Harmonized System codes, are internationally standardized numerical methods of classifying traded products. Developed and maintained by the World Customs Organization (WCO), these codes are used by customs authorities around the world to identify products for tariffs, trade statistics, and other purposes. For exporters of thread rolling machines, the correct application of HS codes is essential for ensuring compliance with global trade regulations and for optimizing logistics and supply chain management.
For thread rolling machines, HS codes typically fall under Chapter 84, which covers machinery and mechanical appliances. This classification includes various types of machinery used in processing metals, of which thread rolling machines are an integral part. It is vital for exporters to accurately classify their products under the correct HS code to avoid delays, penalties, and potential trade barriers.
The Export Market
The export market for thread rolling machines is witnessing a significant upward trend, driven by the increasing demand for high-quality fasteners in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and construction. Countries with robust manufacturing sectors are particularly keen on acquiring advanced thread rolling technology to enhance their production capabilities. Regions such as North America, Europe, and parts of Asia Pacific are leading the way in importing these machines, as manufacturers seek to improve efficiency and reduce production costs.
thread rolling machine hs code exporters
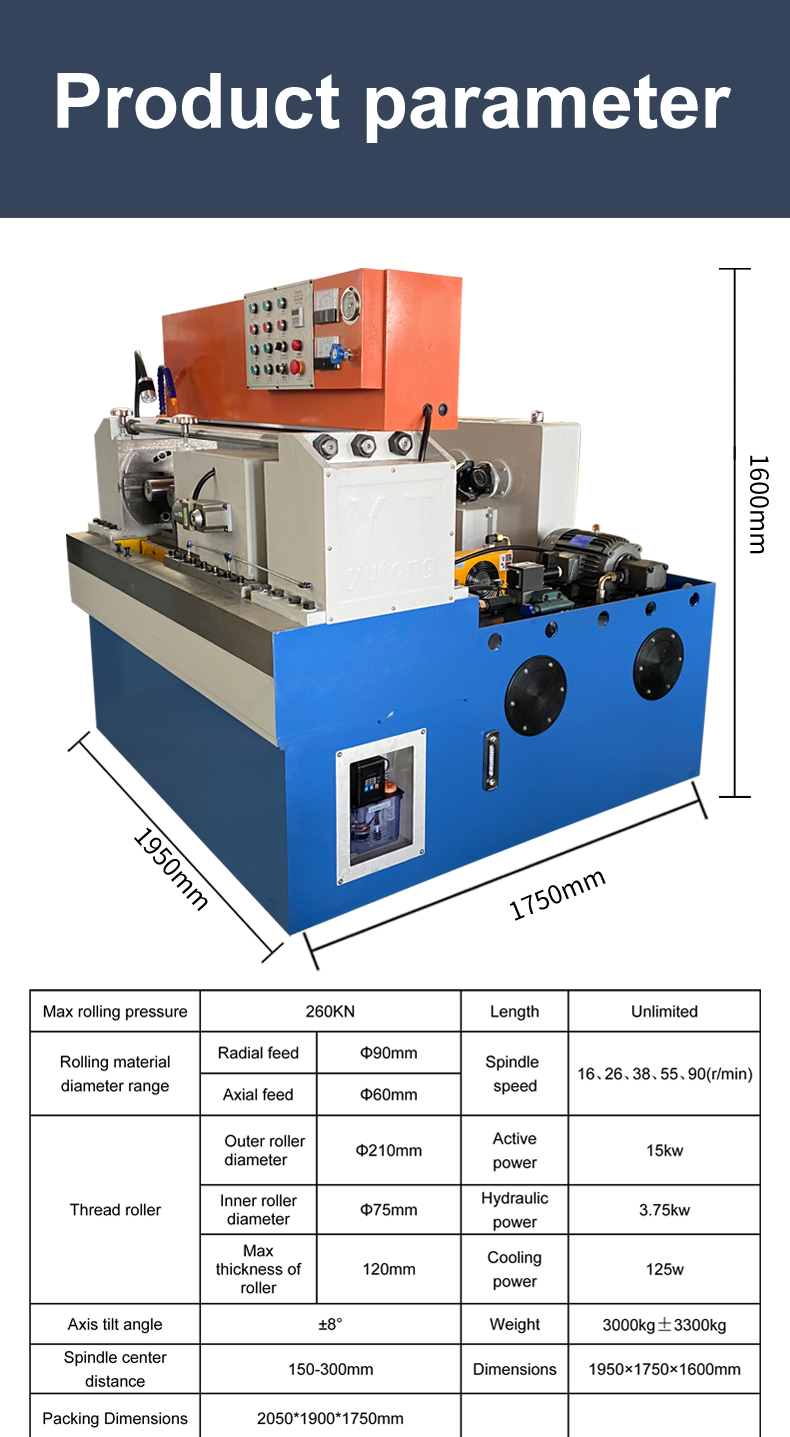
In recent years, countries like China, Germany, and the United States have emerged as key players in the manufacturing and export of thread rolling machines. These nations leverage their technological advancements and rich industrial heritage to produce high-quality machines that meet the evolving needs of various sectors. Exporters from these countries are often at the forefront of innovation, offering customizable solutions that cater to specific customer requirements.
Challenges in Exporting
While the market for thread rolling machines presents impressive opportunities, it is not without challenges. Exporters must navigate a complex landscape of regulations, tariffs, and import restrictions that vary from country to country. Compliance with safety standards, quality certifications, and local regulations is paramount. Additionally, understanding the competitive landscape and pricing strategies in target markets can be a daunting task for exporters.
Furthermore, logistical challenges, such as shipping delays and customs clearance processes, can hinder the smooth flow of goods. Establishing solid relationships with freight forwarders and customs agents can help mitigate these issues and ensure timely delivery to customers.
Conclusion
The export of thread rolling machines is a dynamic and evolving sector, driven by technological advancements and global demand for high-quality machinery. Understanding the nuances of HS codes and ensuring proper classification is vital for exporters aiming to navigate the intricate web of international trade. As manufacturers worldwide continue to seek innovative solutions to enhance their production capabilities, the significance of thread rolling machines and their role in global commerce will undoubtedly grow. By staying informed about market trends and challenges, exporters can strategically position themselves to capitalize on the potential of this lucrative market, ultimately contributing to the growth of the manufacturing industry at large.
