
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Factory Providing Thread Rolling Machine HS Code for Efficient Manufacturing Solutions
Understanding Thread Rolling Machine HS Codes in Factories
In today’s manufacturing landscape, the classification of machinery and tools is crucial for international trade and compliance. One such essential piece of equipment is the thread rolling machine, widely used in various industries to produce fasteners and precision parts. To navigate the intricacies of global trade, it’s vital to understand the Harmonized System (HS) codes that categorize these machines.
What are Thread Rolling Machines?
Thread rolling machines are specialized equipment designed for creating threads on cylindrical workpieces through a cold forming process. This technique involves deforming the material without removing any shavings, resulting in stronger and more precise threads. These machines are widely employed in manufacturing bolts, screws, and other threaded components that are vital in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
Importance of HS Codes
HS codes are standardized numerical methods used to classify traded products. The World Customs Organization (WCO) developed this system to facilitate international trade by providing a universal nomenclature for goods. The codes are crucial in determining tariff duties, trade statistics, and compliance with international regulations. For factories dealing with thread rolling machines, understanding and correctly utilizing the HS codes can prevent costly delays and misunderstandings in customs processes.
Classification of Thread Rolling Machines
The HS code for thread rolling machines falls under the broader category of machine tools. Typically, these machines are classified within Chapter 84 of the HS codes, which covers machinery and mechanical appliances. While the specific code may vary by region, most countries follow a similar classification system. It is essential for manufacturers and exporters to verify the exact codes with their local customs authorities to ensure accurate classification.
Thread rolling machines may be categorized under different sub-categories based on their specifications, such as automatic vs. manual operation, size, production capacity, and additional features like CNC (Computer Numerical Control) capabilities. Proper classification not only aids in compliance with regulations but also impacts the overall cost of importing or exporting the machinery.
Challenges in Classification
thread rolling machine hs code factory
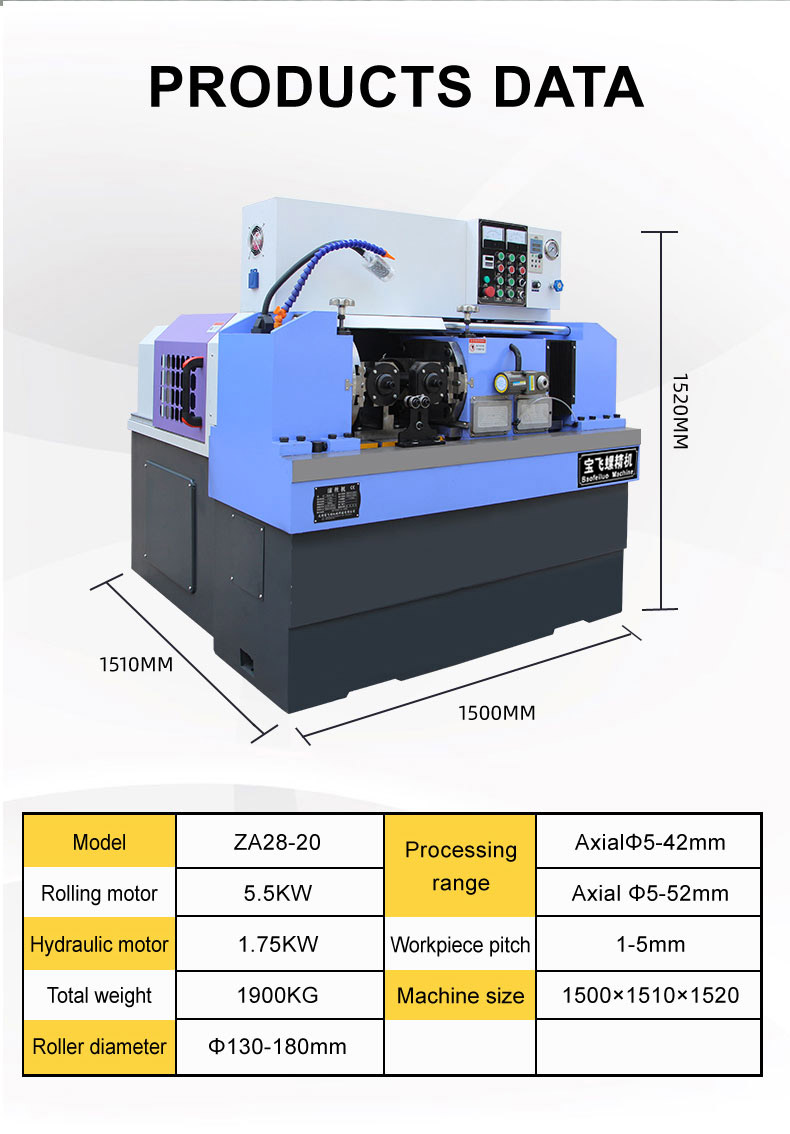
One of the main challenges factories face regarding HS codes is the potential for misclassification. This can lead to increased tariffs, penalties, and delays in shipping. For instance, a factory might mistakenly classify a thread rolling machine as a different type of manufacturing equipment, resulting in incorrect tariff applications. Therefore, factory managers must stay informed about changes in HS code structures and collaborate closely with customs brokers or logistics experts.
Best Practices for Factories
To ensure smooth operations and compliance with HS coding, factories should adopt the following best practices
1. Stay Updated Regularly review updates from local customs authorities and the WCO regarding HS codes for machinery.
2. Training Invest in training for employees involved in export and import processes to enhance their understanding of HS code classification.
3. Documentation Maintain thorough documentation of machinery specifications, operational capabilities, and any modifications made to the equipment.
4. Consult Experts When in doubt, consult with customs brokers or trade compliance experts to ensure accurate classification.
5. Compliance Audits Conduct periodic audits to ensure that all machinery is correctly classified, and necessary documentation is in order.
Conclusion
In summary, the classification of thread rolling machines under HS codes is a critical aspect of international trade for factories. By understanding these codes and implementing best practices, manufacturers can avoid common pitfalls and ensure seamless operations. As global trade continues to evolve, staying informed and compliant will become increasingly vital for success in the manufacturing sector.
