
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
oem types of thread rolling
Understanding OEM Types of Thread Rolling An Overview
Thread rolling is a widely used manufacturing process that creates threads on metal parts through the formation rather than cutting. This method is particularly valued for its ability to produce strong, precise threads with high efficiency. As the need for precision-engineered components continues to grow, especially in sectors like automotive, aerospace, and construction, understanding the various types of OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) thread rolling processes becomes crucial.
The Basics of Thread Rolling
Thread rolling involves the use of two or more hard, cylindrical dies that compress the material to form threads. This method is preferable over traditional cutting because it retains the material's integrity, resulting in stronger threads that can withstand greater wear and tear. The thread rolling process can be classified into three main types flat die rolling, cylindrical die rolling, and planetary rolling.
1. Flat Die Rolling This method uses flat dies that are usually positioned parallel to each other. The workpiece is fed between the dies, which apply pressure to roll the material into the desired thread shape. Flat die rolling is especially effective for producing large batches of identical parts and is often utilized in manufacturing bolts, screws, and other fasteners.
2. Cylindrical Die Rolling In this process, cylindrical dies are used to form threads. The workpiece is rotated between these two dies, allowing the material to flow into the shape of the thread as the dies come together. This technique is suitable for producing external threads and is often deployed for smaller screws and precision components, ensuring uniformity and high dimensional accuracy.
3. Planetary Rolling This advanced technique features a rotating die that orbits around a stationary workpiece. Planetary rolling allows for intricate thread designs and provides excellent surface finishes due to the continuous contact of the die with the material. It's particularly advantageous for high-precision applications such as medical devices and aerospace components.
Advantages of Thread Rolling
The thread rolling process offers several benefits that make it an attractive option for manufacturers
oem types of thread rolling
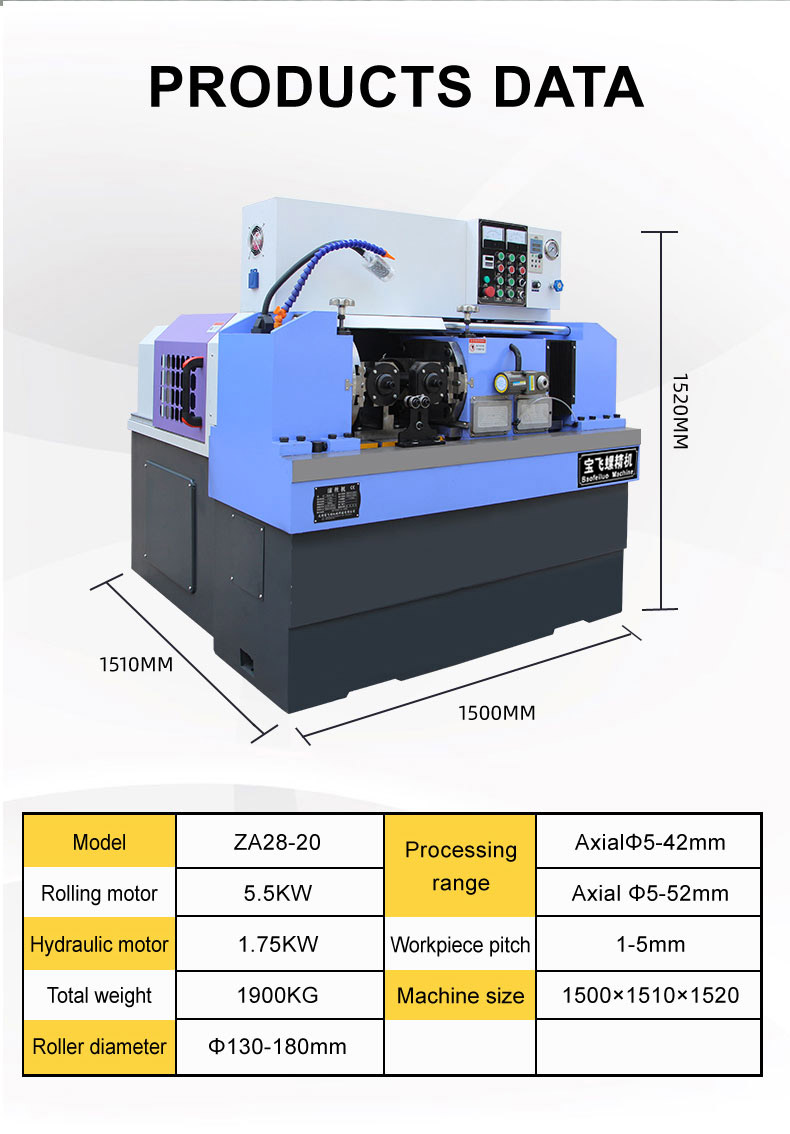
- Enhanced Strength The cold working process involved in thread rolling increases the tensile strength of the material. The continuous grain structure produced during rolling enhances the part's overall durability compared to cut threads.
- Material Efficiency Thread rolling generates less waste than traditional cutting methods. As the material is formed rather than removed, it conserves the raw material and reduces costs associated with scrap.
- Improved Surface Quality Parts produced through thread rolling often have superior surface finishes. This smoothness can lead to better performance in applications where friction and wear resistance are critical.
- High Production Rates Thread rolling is a fast process that allows for the rapid production of large quantities of parts. This efficiency can significantly shorten lead times and meet the demands of just-in-time manufacturing.
Applications of Thread Rolling
Thread rolling is utilized across various industries due to its versatility. In the automotive sector, it is common for manufacturing fasteners like bolts and studs, which require high strength and reliability. The aerospace industry also benefits from this process, as it ensures the integrity of critical components that must endure high-stress conditions.
Moreover, thread rolling plays a significant role in the production of industrial machinery, oilfield equipment, and electronic devices. The consistent quality and precision achieved through this method make it ideal for applications where safety and performance are paramount.
Conclusion
As the manufacturing landscape evolves, the importance of effective and efficient processes like thread rolling cannot be overstated. Understanding the different types of OEM thread rolling techniques empowers manufacturers to select the appropriate method for their specific needs, ensuring high-quality, durable products. As industries continue to innovate and demand higher precision components, thread rolling will remain a key player in the manufacturing process, meeting the challenges of modern engineering head-on.
