
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Jun . 17, 2024 12:46
Back to list
Thread rolling machine HS code.
Harmonized System Codes The Lingua Franca of Global Trade
In the intricate tapestry of international trade, understanding the nuances of classification systems is akin to navigating a ship through treacherous waters. One such system that stands as the compass for global commerce is the Harmonized System (HS) code. This universally accepted standard plays a pivotal role in ensuring seamless transactions across borders, particularly evident in the realm of thread rolling machines – an essential cog in the textile industry's well-oiled machinery.
The HS code system, devised by the World Customs Organization, assigns a unique identifier to every traded product. For thread rolling machines, this code isn't just a sequence of numbers; it's their passport, journeying with them from manufacturer to consumer, crossing language barriers and cultural divides. Envision these robust machines, embodying precision and durability, as they are readied for export. Their HS code becomes their calling card, dictating tariffs, regulations, and even conversations between traders separated by continents and oceans.
But the significance of the HS code extends beyond mere identification. It influences the economic policies and trade agreements that shape global markets. A change in tariff rates based on HS codes can alter the competitive landscape for industries reliant on thread rolling machines. These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes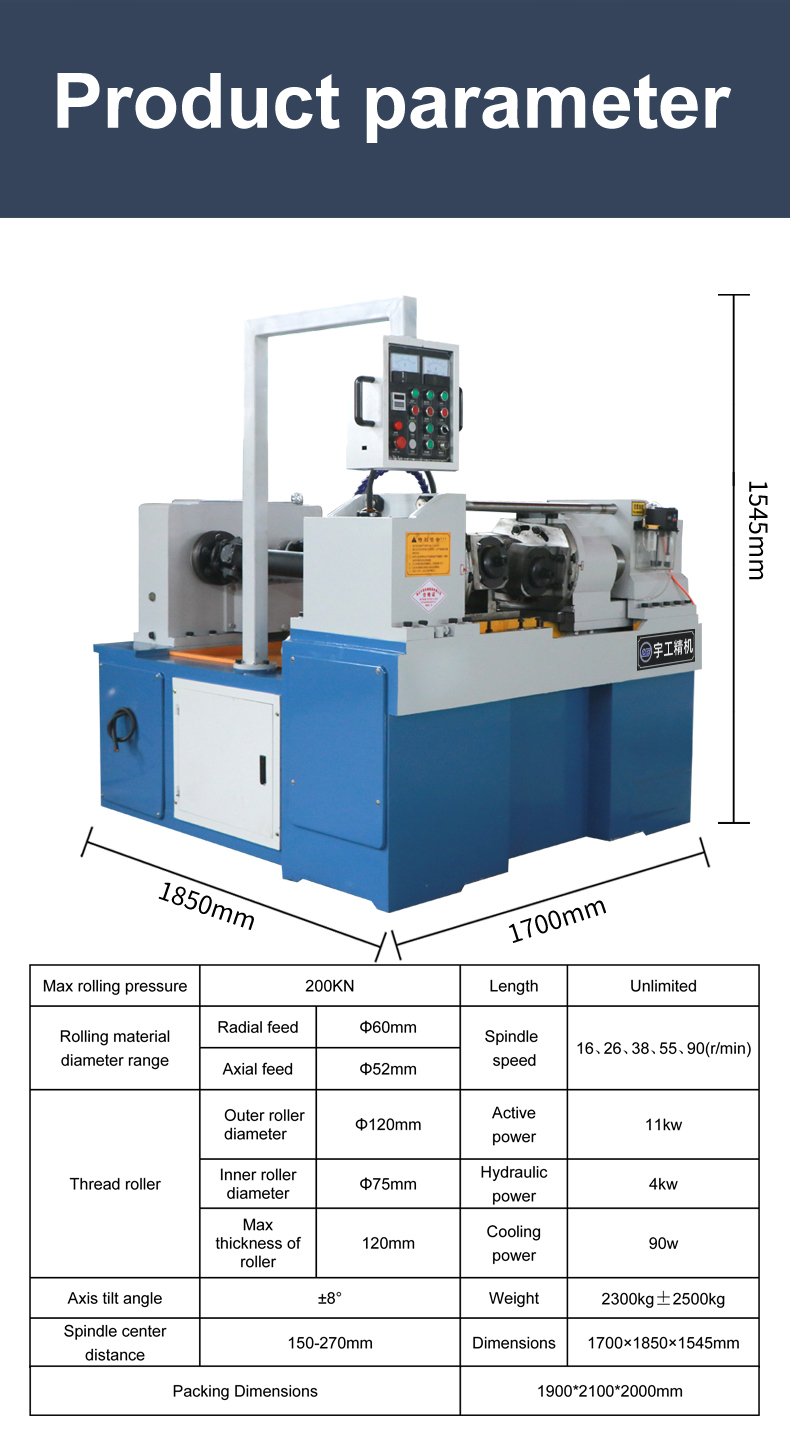 These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes
These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes thread rolling machine hs code. Such adjustments can make or break markets, determine job creation, and reflect a nation's industrial strategy.
Consider the scenario where a country decides to incentivize its domestic textile industry by reducing import duties on thread rolling machines. The tweak in HS codes could spark a revolution, fueling local manufacturing and potentially leading to an export boom. Conversely, an increase in tariffs, reflected in the nomenclature of the HS code, could cripple industries dependent on foreign machinery, sending ripples through the global economy.
In essence, the HS code for thread rolling machines is not merely a static label but a dynamic element that interacts with economic policies, market trends, and international relations. As we zoom out from the intricate coils of thread produced by these machines to the expansive view of global trade, the importance of standardized coding becomes evident. It is the common language that enables understanding and cooperation among trading partners worldwide. Just as thread rolling machines ensure consistency in the textile industry, the HS code system harmonizes the complexities of global commerce, ensuring that the fabric of international trade remains unbroken.
thread rolling machine hs code. Such adjustments can make or break markets, determine job creation, and reflect a nation's industrial strategy.
Consider the scenario where a country decides to incentivize its domestic textile industry by reducing import duties on thread rolling machines. The tweak in HS codes could spark a revolution, fueling local manufacturing and potentially leading to an export boom. Conversely, an increase in tariffs, reflected in the nomenclature of the HS code, could cripple industries dependent on foreign machinery, sending ripples through the global economy.
In essence, the HS code for thread rolling machines is not merely a static label but a dynamic element that interacts with economic policies, market trends, and international relations. As we zoom out from the intricate coils of thread produced by these machines to the expansive view of global trade, the importance of standardized coding becomes evident. It is the common language that enables understanding and cooperation among trading partners worldwide. Just as thread rolling machines ensure consistency in the textile industry, the HS code system harmonizes the complexities of global commerce, ensuring that the fabric of international trade remains unbroken.
 These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes
These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes These devices, designed to transform raw fibers into uniform strands, find their value not just in their functionality but also in the hands of policymakers who wield the power to adjust their HS codes thread rolling machine hs code. Such adjustments can make or break markets, determine job creation, and reflect a nation's industrial strategy.
Consider the scenario where a country decides to incentivize its domestic textile industry by reducing import duties on thread rolling machines. The tweak in HS codes could spark a revolution, fueling local manufacturing and potentially leading to an export boom. Conversely, an increase in tariffs, reflected in the nomenclature of the HS code, could cripple industries dependent on foreign machinery, sending ripples through the global economy.
In essence, the HS code for thread rolling machines is not merely a static label but a dynamic element that interacts with economic policies, market trends, and international relations. As we zoom out from the intricate coils of thread produced by these machines to the expansive view of global trade, the importance of standardized coding becomes evident. It is the common language that enables understanding and cooperation among trading partners worldwide. Just as thread rolling machines ensure consistency in the textile industry, the HS code system harmonizes the complexities of global commerce, ensuring that the fabric of international trade remains unbroken.
thread rolling machine hs code. Such adjustments can make or break markets, determine job creation, and reflect a nation's industrial strategy.
Consider the scenario where a country decides to incentivize its domestic textile industry by reducing import duties on thread rolling machines. The tweak in HS codes could spark a revolution, fueling local manufacturing and potentially leading to an export boom. Conversely, an increase in tariffs, reflected in the nomenclature of the HS code, could cripple industries dependent on foreign machinery, sending ripples through the global economy.
In essence, the HS code for thread rolling machines is not merely a static label but a dynamic element that interacts with economic policies, market trends, and international relations. As we zoom out from the intricate coils of thread produced by these machines to the expansive view of global trade, the importance of standardized coding becomes evident. It is the common language that enables understanding and cooperation among trading partners worldwide. Just as thread rolling machines ensure consistency in the textile industry, the HS code system harmonizes the complexities of global commerce, ensuring that the fabric of international trade remains unbroken. Share:
Latest news
Upgrade Your Production Line With Advanced Threading Solutions
NewsJun.12,2025
Optimize Precision With Advanced Thread Rolling Equipment
NewsJun.12,2025
Maximize Production With A High-Speed Thread Rolling Machine
NewsJun.12,2025
Master Precision Engineering With The Right Roller Threading Machine
NewsJun.12,2025
Find The Right Thread Rolling Tool For Precision Threading
NewsJun.12,2025
Boost Efficiency With Our Thread Rolling Machine
NewsJun.12,2025
