
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
thread rolling machine hsn code products
Understanding the HSN Code for Thread Rolling Machines and Their Products
In the global economy, the classification of goods is paramount for effective taxation, trade, and manufacturing operations. One of the systems employed for this purpose is the Harmonized System Nomenclature (HSN) code. The HSN code is a standardized numerical method of classifying traded products, which helps customs authorities identify products for the purpose of applying appropriate tariffs and taxes. This article delves into the specifics of the HSN code related to thread rolling machines and their associated products, elucidating their significance in both manufacturing and trade.
What is a Thread Rolling Machine?
A thread rolling machine is a specialized piece of equipment used in manufacturing to create threads on various materials, typically metals. Unlike traditional methods that involve cutting threads, thread rolling is a cold forming process where a blank is passed between rollers that imprint the desired thread profile onto the surface. This technique not only enhances the precision of the threads but also improves the mechanical properties of the material, making it stronger due to the work hardening effect.
These machines come in various types, including flat die, cylindrical die, and multi-stage rolling machines. Manufacturers use them to produce components with threads that are essential in numerous applications, from automotive parts to construction materials.
The Importance of HSN Codes
The HSN code system simplifies international trade by reducing complexities in customs processes. This standardization is crucial in determining tariff rates, facilitating more straightforward import and export procedures across different countries. The specificity of HSN codes allows businesses to classify their goods accurately, reducing the risk of misclassification that can lead to legal issues or financial penalties.
HSN Code for Thread Rolling Machines
thread rolling machine hsn code products
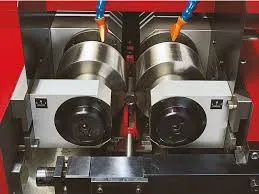
For thread rolling machines, the HSN code typically falls under the broader category of machinery used for working metal. In the Indian context, for example, the relevant HSN code for thread rolling machines is 8462. This section encompasses various types of machine tools, including those used specifically for the processing of metal, which includes thread rolling equipment.
This categorization plays a vital role for manufacturers and suppliers involved in the production and distribution of these machines. Understanding the correct HSN code is essential not only for compliance with tax obligations but also for maintaining accurate inventory records, facilitating international shipping, and ensuring that the end products meet requisite standards.
Products Associated with Thread Rolling Machines
Thread rolling machines are used to manufacture a wide array of products that are integral to several industries. Examples of products created using these machines include
1. Bolts and Nuts Essential fasteners used in construction, automotive, and machinery applications. 2. Screws Utilized in various assembly processes, from furniture manufacturing to electronics. 3. Studs Commonly used in structural applications where strong attachment points are needed. 4. Threaded Rods Often used in scaffolding, engineering structures, and other applications requiring strength and stability.
Each of these products also has its own specific HSN code, which allows customs authorities to manage and track trade efficiently. Knowing these codes is crucial for businesses engaged in international trading, as it affects pricing, duties, and the overall competitiveness of their products in the global market.
Conclusion
The HSN code for thread rolling machines and their associated products plays a crucial role in the manufacturing and trade sectors. By understanding this framework, businesses can navigate the complexities of international trade, comply with regulations, and optimize their operations. As the global marketplace continues to evolve, adopting such standardized systems ensures that manufacturers remain competitive and efficient while facilitating smoother trade interactions across borders. Whether you are a manufacturer, exporter, or importer, being well-versed in the HSN code relevant to your products is not just an obligation but a strategic advantage.
