
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
thread rolling machines
Understanding Thread Rolling Machines A Vital Tool in Manufacturing
Thread rolling machines play a crucial role in modern manufacturing processes, particularly in the production of fasteners and various threaded components. This article delves into the functionalities, advantages, and applications of thread rolling machines, demonstrating how they enhance efficiency and precision in manufacturing.
What is a Thread Rolling Machine?
Thread rolling machines are specialized equipment designed to create threads on cylindrical materials through a non-cutting process. The primary mechanism involves the use of hardened rollers, which deform the surface of the material to produce threads. Unlike traditional cutting methods, thread rolling is a cold forming process that leaves the material intact, ensuring superior strength and durability.
The machines can vary in design, from simple manual models to complex automatic systems. Most commonly, they feature two or three rollers that rotate around the workpiece, pressing against it to form the desired thread profile. The process can be done on various materials, including steel, aluminum, and brass, making it highly versatile for different manufacturing needs.
The Advantages of Thread Rolling
1. Enhanced Strength and Durability One of the most significant benefits of thread rolling is that it produces threads with greater tensile strength than those created by machining. The cold forming process aligns the grain structure of the metal, resulting in stronger, more durable threads that can better withstand stress and wear.
2. Improved Surface Finish Thread rolling machines provide superior surface finishes. The process leaves behind a smooth, polished surface that often requires little to no additional finishing. This is crucial in various applications, particularly in industries where thread contamination could lead to failure.
3. Material Efficiency Thread rolling is a highly material-efficient process. Unlike traditional machining, which removes a considerable amount of material to create threads, rolling displaces the material to form the threads, generating less waste. This efficiency not only reduces material costs but also benefits the environment by minimizing scrap.
thread rolling machines
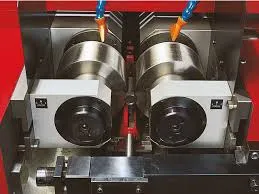
4. High Production Rates Thread rolling machines are capable of producing large quantities of threads in a relatively short amount of time. Their automated systems can increase throughput, making them ideal for mass production environments. This rapid production leads to lower labor costs and shorter lead times, which are critical in today’s fast-paced manufacturing world.
5. Versatility These machines can create various thread types and sizes, from fine threads for delicate applications to larger threads for heavy-duty uses. This versatility allows manufacturers to meet diverse client specifications without the need for multiple machines.
Applications of Thread Rolling Machines
Thread rolling machines are extensively used in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and construction. In the aerospace sector, for example, the demand for lightweight, high-strength fasteners is vital; thread rolling provides the necessary strength-to-weight ratio. Similarly, in the automotive industry, fasteners for engines and other critical components benefit from the enhanced durability offered by rolled threads.
In the oil and gas sector, companies require robust threads that can withstand extreme environments. Thread rolling delivers on this need by ensuring that the products are both strong and resistant to corrosion.
Moreover, in construction, threaded rods and anchors are routinely produced using thread rolling due to the process’s efficiency and ability to provide high-quality threads suitable for structural applications.
Conclusion
In summary, thread rolling machines are indispensable tools in many manufacturing sectors, offering an array of benefits that include enhanced strength, improved surface finish, material efficiency, high production rates, and versatility. As industries continue to evolve and the demand for high-quality threaded components rises, the importance of thread rolling technology will only grow. Manufacturers who invest in these machines can expect not only to enhance their production capabilities but also to maintain a competitive edge in the marketplace. As technology progresses, we can anticipate further innovations in thread rolling processes, leading to even greater efficiencies and outcomes in threaded component manufacturing.
