
-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
types of thread rolling machine products
Types of Thread Rolling Machine Products
Thread rolling is a manufacturing process used to create specific shapes and features on workpieces, particularly threads, by deforming the material rather than cutting it. This method boasts numerous advantages including increased strength, enhanced surface finish, and improved dimensional accuracy. In the realm of manufacturing and engineering, thread rolling machines come in various configurations tailored to different applications. Below, we explore the primary types of thread rolling machine products and their unique features.
1. Flat Die Thread Rolling Machines
Flat die thread rolling machines utilize two flat dies to exert force on the workpiece. These machines are particularly well-suited for producing external threads on cylindrical parts, such as bolts and screws. The process involves the rotation of the workpiece between the dies, which apply pressure in a specified direction to form the thread. Flat die machines are known for their simplicity, ease of operation, and ability to process a wide range of materials, including metals and plastics. They are commonly used in high-volume production settings due to their efficiency.
2. Planetary Thread Rolling Machines
Planetary thread rolling machines operate on a different principle by employing multiple rolling heads that move in a circular pattern around the workpiece. This design allows for the simultaneous processing of several threads, making it ideal for high-output production runs. The key advantage of the planetary system is the ability to create very precise threads and unique configurations, which would be challenging with other machine types. These machines are versatile and can be used for both external and internal threads, catering to an extensive variety of industries, including automotive and aerospace applications.
3. Screw Thread Rolling Machines
types of thread rolling machine products
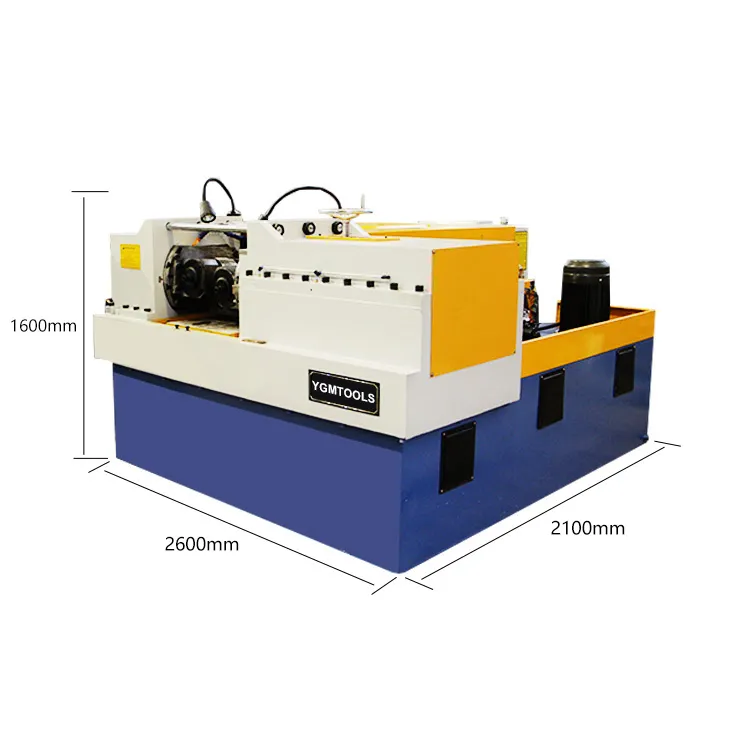
Specifically designed for creating screw threads, these machines can generate threads with high precision and are critical in industries that require high-quality fasteners. Screw thread rolling machines can handle both continuous and batch production, and they often feature advanced control systems to ensure accuracy throughout the rolling process. The flexibility of these machines allows manufacturers to adapt to different specifications and standards, making them a valuable asset in thread manufacturing.
4. Rotary Thread Rolling Machines
Rotary thread rolling machines use a rotating motion to form threads, moving the dies around the workpiece while it remains stationary. This method is efficient for producing threads on long, continuous parts such as rods and bars. The design of rotary machines allows them to accommodate various sizes and lengths of materials, making them worth considering for companies that need flexibility in their production lines. These machines can create a range of thread forms, enhancing their applicability across different industrial sectors.
5. CNC Thread Rolling Machines
As industrial automation progresses, CNC (Computer Numerical Control) thread rolling machines have gained popularity. These machines integrate advanced technology to offer high precision and automation in the rolling process. CNC thread rolling machines can be programmed to perform various thread profiles and patterns, minimizing human error and maximizing efficiency. The ability to quickly change settings and designs allows manufacturers to respond rapidly to market demands, making CNC machines a preferred choice for modern manufacturing environments.
Conclusion
The world of thread rolling machines is diverse, offering a multitude of options tailored to specific thread production needs. From flat die machines for simple applications to advanced CNC machines capable of complex patterns, each type serves its purpose within the manufacturing process. As industries evolve and technology advances, the demand for reliable, efficient thread rolling machines will undoubtedly continue to grow, driving innovation and improvements in design and functionality. Understanding the characteristics and advantages of each type can help manufacturers choose the right machine to enhance their productivity and product quality in the competitive marketplace.
